JAVA实验3《对象和类》
一、实验目的
1.设计类,并画出UML类图
2.实现UML中的类
3.使用类开发应用程序
二、实验内容
1、(P305, 9.1)【矩形类Rectangle】遵照9.2节中Circle类的例子,设计一个名为Rectangle的类表示矩形。这个类包括:
两个名为width和height的double型数据域,它们分别表示矩形的宽和高。width和height的默认值都为1。
创建默认矩形的无参构造方法。
创建width和height为指定值的矩形的构造方法。
一个名为getArea()的方法返回这个矩形的面积。
一个名为getPerimeter()的方法返回矩形周长。
画出该类的UML图并实现这个类。编写一个测试程序,创建两个Rectangle对象:一个矩形的宽为4高为40,另一个矩形的宽为3.5高为35.9。依次显示每个矩形的宽、高、面积和周长。
Rectangle
Width:double
Height:double
+Rectangle()
+Rectangle(width:double ,height:double )
+getArea():double
+getPermeter():double
实验报告:
(1).实验结果与分析:
UML图:

实验结构截图:
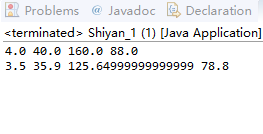
结果分析:依次显示每个矩形的宽、高、面积和周长
(2).心得体会:
通过这次实验,让我对类的运用的更加的熟练
(3).源代码:
public class Shiyan_1 {
public static void main (String [] args) {
Rectangle rectangle1 = new Rectangle(4,40);
Rectangle rectangle2 = new Rectangle(3.5,35.9);
System.out.println(rectangle1.width+" "+rectangle1.height+" "+rectangle1.getArea()+" "+rectangle1.getPermeter());
System.out.println(rectangle2.width+" "+rectangle2.height+" "+rectangle2.getArea()+" "+rectangle2.getPermeter());
}
}
class Rectangle{
double width = 1;
double height = 1;
Rectangle(){
}
Rectangle(double width,double height){
this.height = height;
this.width = width;
}
double getArea() {
return width*height;
}
double getPermeter() {
return 2*(width+height);
}
}
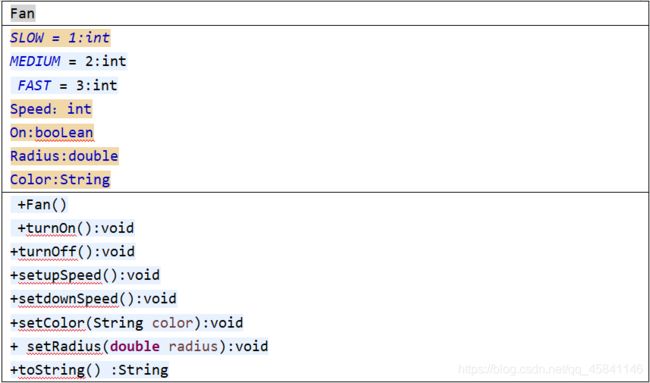
- (P307, 9.8)【风扇类Fan】设计一个名为Fan的类表示一个风扇。这个类包括:
三个名为SLOW、MEDIUM和FAST而值为1、2、3的常量表示风扇的速度。
一个名为speed的int类型私有数据域表示风扇的速度(默认值为SLOW)。
一个名为on的boolean类型私有数据域表示风扇是否打开(默认值为false)。
一个名为radius的double类型私有数据域表示风扇的半径(默认值为5)。
一个名为color的String类型私有数据域表示风扇的颜色(默认值为blue)。
这四个数据域的访问器和修改器。
一个创建默认风扇的无参构造方法。
一个名为toString()的方法返回描述风扇的字符串。如果风扇是打开的,那么该方法在一个组合的字符串中返回风扇的速度、颜色和半径。如果风扇没有打开,该方法返回一个由“fan is off”和风扇颜色、半径组成的字符串。
画出该类的UML图。实现这个类。编写一个测试程序,创建两个Fan对象。将第一个对象设置为最大速度、半径为10、颜色为yellow、状态为打开。将第二个对象设置为中等速度、半径为5、颜色为blue、状态为关闭。通过调用它们的toString方法显示这些对象。
实验报告:
(1).实验结果与分析:
UML图:
实验结果截图:

结果分析:
将第一个对象设置为最大速度、半径为10、颜色为yellow、状态为打开。将第二个对象设置为中等速度、半径为5、颜色为blue、状态为关闭。
(2).心得体会:
通过这次实验让我对类的运用更加的熟练,对公共域和私有域也有一定的掌握。
(3).源代码:
public class Shiyan_2 {
public static void main (String [] args) {
Fan fan1 = new Fan();
Fan fan2 = new Fan();
fan1.turnOn();
fan1.setupSpeed();
fan1.setupSpeed();
fan1.setColor("yellow");
fan1.setRadius(10);
System.out.println("fan1 's "+fan1.toString());
fan2.setupSpeed();
System.out.println("fan2 's "+fan2.toString());
}
}
class Fan{
public static int SLOW = 1;
public static int MEDIUM = 2;
public static int FAST = 3;
private int speed = SLOW;
private boolean on = false;
private double radius = 5;
private String color = "blue";
public Fan() {
}
public void turnOn() {
on = true;
}
public void turnOff() {
on = false;
}
public void setupSpeed() {
if(on&&speed<3) {
speed++;
}
}
public void setdownSpeed(){
if(on&&speed>1) {
speed--;
}
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public String toString() {
if(on) {
return "speed is "+speed+" color is "+color+" radius is "+radius;
}
else
return "fan is off";
}
}
3.(P308,9.10*)【二次方程式】为二次方程式ax2+bx+c=0设计一个名为QuadraticEquation的类。这个类包括:
代表三个系数的私有数据域a、b、c。
一个参数为a、b、c的构造方法。
a、b、c的三个get方法。
一个名为getDiscriminant()的方法返回判别式,b2-4ac。
一个名为getRoot1()和getRoot2()的方法返回等式的两个根。
这些方法只有在判别式为非负数时才有用。如果判别式为负,方法返回0。
画出该类的UML图。实现这个类。编写一个测试程序,提示用户输入a、b、c的值,然后显示判别式的结果。如果判别式为正数,显示两个根;如果判别式为0,显示一个根;否则,显示“The equation has no roots”。
实验报告:
(1).实验结果和分析:
UML图:
实验结果分析
提示用户输入a、b、c的值,然后显示判别式的结果。如果判别式为正数,显示两个根;如果判别式为0,显示一个根;否则,显示“The equation has no roots”
(2).源代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Shiyan_3 {
public static void main (String [] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
double a = input.nextDouble();
double b = input.nextDouble();
double c = input.nextDouble();
if(a==0) {
System.out.println(-c/b);
System.exit(0);
}
QuadraticEquation quadraticEquation1 = new QuadraticEquation(a,b,c);
if(quadraticEquation1.getDiscriminant(a, b, c)>0)
System.out.println(quadraticEquation1.getRoot1()+" "+quadraticEquation1.getRoot2());
else if(quadraticEquation1.getDiscriminant(a, b, c)==0)
System.out.println(quadraticEquation1.getRoot1());
else
System.out.println("The equation has no roots");
}
}
class QuadraticEquation{
private double a,b,c;
public QuadraticEquation(double a,double b,double c) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
public double getDiscriminant(double a,double b,double c) {
return b*b-4*a*c;
}
public double getRoot1() {
return (-b+Math.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c))/(2*a);
}
public double getRoot2() {
return (-b-Math.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c))/(2*a);
}
}
(3).心得体会:
通过本次实验让我对类的理解和类的运用更加深刻,类中的private域是无法在主函数中被调用的。
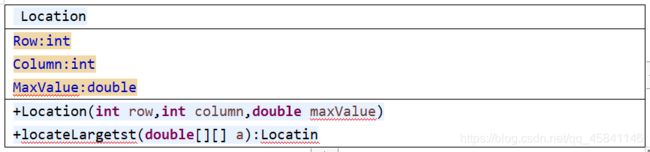
4.(P308, 9.13**)【位置类】设计一个名为Location的类,定位二维数组中的最大值及其位置。这个类包括公共的数据域row、column和maxValue,二维数组中的最大值及其下标用double型的maxValue以及int型的row和column存储。
编写下面的方法,返回一个二维数组中最大值的位置。
public static Location locateLargetst(double[][] a)
返回值是一个Location的实例。编写一个测试程序,提示用户输入一个二维数组,然后显示这个数组中的最大元素及下标。运行实例如下:
输入二维数组的行数和列数: 3 4
输入数组:
23.5 35 2 10
4.5 3 45 3.5
35 44 5.5 9.6
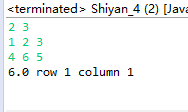
最大元素及其下标是: 45 在(1,2)
实验报告:
(1).实验结果与分析:
UML图:
实验结果分析:
提示用户输入一个二维数组,然后显示这个数组中的最大元素及下标。
(2).心得体会:
通过本次实验,我对类的一些运用掌握的更加熟练,相信在今后遇到一些关于类的问题我也能迎刃而解。
(3).源代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Shiyan_4 {
public static void main (String [] args) {
int i,j,maxValue=0;
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int row = input.nextInt();
int column= input.nextInt();
double[][]a = new double[row][column];
for(i=0;i<row;i++) {
for(j=0;j<column;j++) {
a[i][j] = input.nextDouble();
}
}
Location Loc = Location.locateLargetst(a);
System.out.println(Loc.maxValue+" row "+Loc.row+" column "+Loc.column);
}
}
class Location{
public int row=0;
public int column=0;
public double maxValue;
public Location(int row,int column,double maxValue) {
this.row = row;
this.column = column;
this.maxValue = maxValue;
}
public static Location locateLargetst(double[][] a) {
int row1=0,column1=0;
int row2=0,column2=0;
double maxValue = a[0][0];
for(row1=0;row1<a.length;row1++) {
for(column1=0;column1<a[row1].length;column1++) {
if(maxValue<a[row1][column1]) {
maxValue = a[row1][column1];
row2 = row1;
column2 = column1;
}
}
}
Location Location1 = new Location(row2,column2,maxValue);
return Location1;
}
}