Go实战--golang中使用JWT(JSON Web Token)
生命不止,继续 go go go !!!
之前写过关于golang中如何使用cookie的博客:
实战–go中使用cookie
今天就来跟大家简单介绍一下golang中如何使用token,当然是要依赖一下github上的优秀的开源库了。
首先,要搞明白一个问题,token、cookie、session的区别。
##token、cookie、session的区别
Cookie
Cookie总是保存在客户端中,按在客户端中的存储位置,可分为内存Cookie和硬盘Cookie。
内存Cookie由浏览器维护,保存在内存中,浏览器关闭后就消失了,其存在时间是短暂的。硬盘Cookie保存在硬盘里,有一个过期时间,除非用户手工清理或到了过期时间,硬盘Cookie不会被删除,其存在时间是长期的。所以,按存在时间,可分为非持久Cookie和持久Cookie。
cookie 是一个非常具体的东西,指的就是浏览器里面能永久存储的一种数据,仅仅是浏览器实现的一种数据存储功能。
cookie由服务器生成,发送给浏览器,浏览器把cookie以key-value形式保存到某个目录下的文本文件内,下一次请求同一网站时会把该cookie发送给服务器。由于cookie是存在客户端上的,所以浏览器加入了一些限制确保cookie不会被恶意使用,同时不会占据太多磁盘空间,所以每个域的cookie数量是有限的。
Session
session 从字面上讲,就是会话。这个就类似于你和一个人交谈,你怎么知道当前和你交谈的是张三而不是李四呢?对方肯定有某种特征(长相等)表明他就是张三。
session 也是类似的道理,服务器要知道当前发请求给自己的是谁。为了做这种区分,服务器就要给每个客户端分配不同的“身份标识”,然后客户端每次向服务器发请求的时候,都带上这个“身份标识”,服务器就知道这个请求来自于谁了。至于客户端怎么保存这个“身份标识”,可以有很多种方式,对于浏览器客户端,大家都默认采用 cookie 的方式。
服务器使用session把用户的信息临时保存在了服务器上,用户离开网站后session会被销毁。这种用户信息存储方式相对cookie来说更安全,可是session有一个缺陷:如果web服务器做了负载均衡,那么下一个操作请求到了另一台服务器的时候session会丢失。
Token
token的意思是“令牌”,是用户身份的验证方式,最简单的token组成:uid(用户唯一的身份标识)、time(当前时间的时间戳)、sign(签名,由token的前几位+盐以哈希算法压缩成一定长的十六进制字符串,可以防止恶意第三方拼接token请求服务器)。还可以把不变的参数也放进token,避免多次查库
这里的token是指SON Web Token:
JSON Web Token (JWT) is a compact URL-safe means of representing claims to be transferred between two parties. The claims in a JWT are encoded as a JSON object that is digitally signed using JSON Web Signature (JWS).
使用JWT进行认证
JSON Web Tokens (JWT) are a more modern approach to authentication.
As the web moves to a greater separation between the client and server, JWT provides a wonderful alternative to traditional cookie based authentication models.
JWTs provide a way for clients to authenticate every request without having to maintain a session or repeatedly pass login credentials to the server.
用户注册之后, 服务器生成一个 JWT token返回给浏览器, 浏览器向服务器请求数据时将 JWT token 发给服务器, 服务器用 signature 中定义的方式解码
JWT 获取用户信息.
一个 JWT token包含3部分:
- header: 告诉我们使用的算法和 token 类型
- Payload: 必须使用 sub key 来指定用户 ID, 还可以包括其他信息比如 email, username 等.
- Signature: 用来保证 JWT 的真实性. 可以使用不同算法

##JWT应用
上面说了那么多,接下来就是要coding了。
用到的开源库:
github.com/codegangsta/negroni
Idiomatic HTTP Middleware for Golang
http的一个中间件
github.com/dgrijalva/jwt-go
Golang implementation of JSON Web Tokens (JWT)
github.com/dgrijalva/jwt-go/request
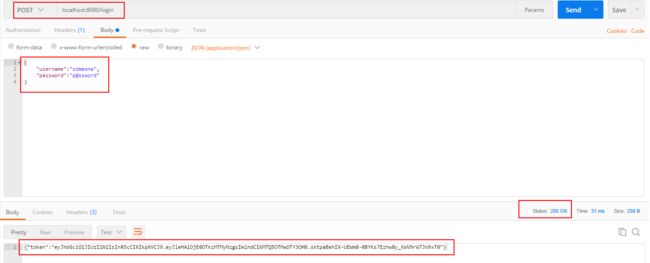
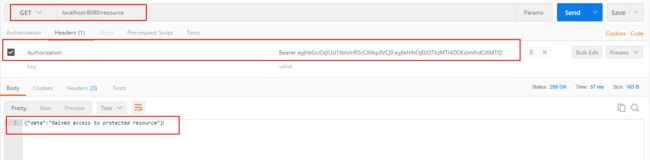
这里分两个api,一个是通过login获取token,然后根据token访问另一个api。首先看看login是如何生成token的:
当然首先是验证用户名和密码,为了节省篇幅这里只是代码片段,完整代码最后献上。
token := jwt.New(jwt.SigningMethodHS256)
claims := make(jwt.MapClaims)
claims["exp"] = time.Now().Add(time.Hour * time.Duration(1)).Unix()
claims["iat"] = time.Now().Unix()
token.Claims = claims
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Error extracting the key")
fatal(err)
}
tokenString, err := token.SignedString([]byte(SecretKey))
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Error while signing the token")
fatal(err)
}
接下来就是验证token的中间件了:
token, err := request.ParseFromRequest(r, request.AuthorizationHeaderExtractor,
func(token *jwt.Token) (interface{}, error) {
return []byte(SecretKey), nil
})
if err == nil {
if token.Valid {
next(w, r)
} else {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusUnauthorized)
fmt.Fprint(w, "Token is not valid")
}
} else {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusUnauthorized)
fmt.Fprint(w, "Unauthorized access to this resource")
}
最后完整代码:
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"strings"
"time"
"github.com/codegangsta/negroni"
"github.com/dgrijalva/jwt-go"
"github.com/dgrijalva/jwt-go/request"
)
const (
SecretKey = "welcome to wangshubo's blog"
)
func fatal(err error) {
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
type UserCredentials struct {
Username string `json:"username"`
Password string `json:"password"`
}
type User struct {
ID int `json:"id"`
Name string `json:"name"`
Username string `json:"username"`
Password string `json:"password"`
}
type Response struct {
Data string `json:"data"`
}
type Token struct {
Token string `json:"token"`
}
func StartServer() {
http.HandleFunc("/login", LoginHandler)
http.Handle("/resource", negroni.New(
negroni.HandlerFunc(ValidateTokenMiddleware),
negroni.Wrap(http.HandlerFunc(ProtectedHandler)),
))
log.Println("Now listening...")
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)
}
func main() {
StartServer()
}
func ProtectedHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
response := Response{"Gained access to protected resource"}
JsonResponse(response, w)
}
func LoginHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
var user UserCredentials
err := json.NewDecoder(r.Body).Decode(&user)
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden)
fmt.Fprint(w, "Error in request")
return
}
if strings.ToLower(user.Username) != "someone" {
if user.Password != "p@ssword" {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden)
fmt.Println("Error logging in")
fmt.Fprint(w, "Invalid credentials")
return
}
}
token := jwt.New(jwt.SigningMethodHS256)
claims := make(jwt.MapClaims)
claims["exp"] = time.Now().Add(time.Hour * time.Duration(1)).Unix()
claims["iat"] = time.Now().Unix()
token.Claims = claims
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Error extracting the key")
fatal(err)
}
tokenString, err := token.SignedString([]byte(SecretKey))
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Error while signing the token")
fatal(err)
}
response := Token{tokenString}
JsonResponse(response, w)
}
func ValidateTokenMiddleware(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request, next http.HandlerFunc) {
token, err := request.ParseFromRequest(r, request.AuthorizationHeaderExtractor,
func(token *jwt.Token) (interface{}, error) {
return []byte(SecretKey), nil
})
if err == nil {
if token.Valid {
next(w, r)
} else {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusUnauthorized)
fmt.Fprint(w, "Token is not valid")
}
} else {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusUnauthorized)
fmt.Fprint(w, "Unauthorized access to this resource")
}
}
func JsonResponse(response interface{}, w http.ResponseWriter) {
json, err := json.Marshal(response)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
w.Write(json)
}