数据结构_堆_Java中的实现类
1.数据结构:堆(Heap)
https://www.jianshu.com/p/6b526aa481b1
2.Java实现最大堆
https://www.jianshu.com/p/257820688bf1
3.java借助PriorityQueue实现小根堆和大根堆
https://blog.csdn.net/zcf1784266476/article/details/68961473
我们先来了解下堆的基本概念:
基本概念
堆就是用数组实现的二叉树,所有它没有使用父指针或者子指针。堆根据“堆属性”来排序,“堆属性”决定了树中节点的位置。
堆的常用方法:
- 构建优先队列
- 支持堆排序
- 快速找出一个集合中的最小值(或者最大值)
堆属性
堆分为两种:最大堆和最小堆,两者的差别在于节点的排序方式。
在最大堆中,父节点的值比每一个子节点的值都要大。在最小堆中,父节点的值比每一个子节点的值都要小。这就是所谓的“堆属性”,并且这个属性对堆中的每一个节点都成立。
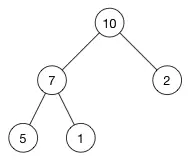
例子:
这是一个最大堆,,因为每一个父节点的值都比其子节点要大。10 比 7 和 2 都大。7 比 5 和 1都大。
根据这一属性,那么最大堆总是将其中的最大值存放在树的根节点。而对于最小堆,根节点中的元素总是树中的最小值。堆属性非常的有用,因为堆常常被当做优先队列使用,因为可以快速的访问到“最重要”的元素。
注意:
堆的根节点中存放的是最大或者最小元素,但是其他节点的排序顺序是未知的。例如,在一个最大堆中,最大的那一个元素总是位于 index 0 的位置,但是最小的元素则未必是最后一个元素。唯一能够保证的是最小的元素是一个叶节点,但是不确定是哪一个。
Java中的实现
借助Java 中的类 PriorityQueue 可以实现小根堆和大根堆。
/**
* An unbounded priority {@linkplain Queue queue} based on a priority heap.
* The elements of the priority queue are ordered according to their
* {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering}, or by a {@link Comparator}
* provided at queue construction time, depending on which constructor is
* used. A priority queue does not permit {@code null} elements.
* A priority queue relying on natural ordering also does not permit
* insertion of non-comparable objects (doing so may result in
* {@code ClassCastException}).
*
* The head of this queue is the least element
* with respect to the specified ordering. If multiple elements are
* tied for least value, the head is one of those elements -- ties are
* broken arbitrarily. The queue retrieval operations {@code poll},
* {@code remove}, {@code peek}, and {@code element} access the
* element at the head of the queue.
*
*
A priority queue is unbounded, but has an internal
* capacity governing the size of an array used to store the
* elements on the queue. It is always at least as large as the queue
* size. As elements are added to a priority queue, its capacity
* grows automatically. The details of the growth policy are not
* specified.
通过上面介绍,可以看到第一个元素,就是这个排序的最后一个元素。
下面我们看下PriorityQueue 的具体使用:
package leetcode;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
/**
* Created by szh on 2020/6/21.
* @author szh
*/
public class HeapTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
PriorityQueue minPriorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(10, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1.compareTo(o2);
}
});
int[] result_1 = new int[]{1, 2, 4, 3, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2};
for(int tmp : result_1){
minPriorityQueue.offer(tmp);
}
while(minPriorityQueue.size()>0){
System.out.println(minPriorityQueue.poll());
}
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
PriorityQueue maxPriorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(10, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return -o1.compareTo(o2);
}
});
int[] result_2 = new int[]{1, 2, 4, 3, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2};
for(int tmp : result_2){
maxPriorityQueue.offer(tmp);
}
while(maxPriorityQueue.size()>0){
System.out.println(maxPriorityQueue.poll());
}
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
}
}
输出:
1
2
2
2
2
2
2
3
4
-------------------------------
-------------------------------
-------------------------------
4
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
-------------------------------
-------------------------------
-------------------------------