SpringSecurity学习笔记(2)自定义表单登录
前言
SpringSecurity的默认登录页面不够好看,我们完全可以自定义登录表单
准备工作
前后端不分离情况下的配置
//放行一部分文件
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
web.ignoring().antMatchers("/js/**","/css/**","/images/**");
}
//配置登录页
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()//开启配置
.anyRequest().authenticated()//任何请求都要认证后才能访问
.and()//回到了authorizeRequests()
.formLogin()//配置表单登录
.loginPage("/login.html")//配置登录页和默认的登录接口
.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin") //配置登录接口,名字要与前端对应
.usernameParameter("name")//默认是username,手动配置要与前端对应
.passwordParameter("pwd")//默认是password,手动配置要与前端对应
.successForwardUrl("/user/1")//登录成功跳转到指定页面,不指定默认跳转到/,这是一个转发
.defaultSuccessUrl("/user/1")//这是一个重定向,与上面二者取一就可以
.failureForwardUrl("/login")//失败转发
.failureUrl("/login")//失败重定向
.permitAll()//表示和登录相关的请求都放行
.and()
.logout()
.logoutUrl("/logout")//默认注销的 URL 是 /logout,是一个 GET 请求,我们可以通过 logoutUrl 方法来修改默认的注销 URL。
.logoutRequestMatcher(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout","POST"))//logoutRequestMatcher 方法不仅可以修改注销 URL,还可以修改请求方式,实际项目中,这个方法和 logoutUrl 任意设置一个即可。
.logoutSuccessUrl("/index")//logoutSuccessUrl 表示注销成功后要跳转的页面。
.deleteCookies()//deleteCookies 用来清除 cookie。
.clearAuthentication(true)
.invalidateHttpSession(true)
//clearAuthentication 和 invalidateHttpSession 分别表示清除认证信息和使 HttpSession 失效,默认可以不用配置,默认就会清除
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
前后端分离的情况
登录方式
有状态登录
有状态服务,即服务端需要记录每次会话的客户端信息,从而识别客户端身份,根据用户身份进行请求的处理,典型的设计如 Tomcat 中的 Session。例如登录:用户登录后,我们把用户的信息保存在服务端 session 中,并且给用户一个 cookie 值,记录对应的 session,然后下次请求,用户携带 cookie 值来(这一步有浏览器自动完成),我们就能识别到对应 session,从而找到用户的信息。这种方式目前来看最方便,但是也有一些缺陷,服务端保存大量数据,增加服务端压力;服务端保存用户状态,不支持集群化部署
无状态登录
微服务集群中的每个服务,对外提供的都使用 RESTful 风格的接口。而 RESTful 风格的一个最重要的规范就是:服务的无状态性,即:
- 服务端不保存任何客户端请求者信息
- 客户端的每次请求必须具备自描述信息,通过这些信息识别客户端身份
优点:
- 客户端请求不依赖服务端的信息,多次请求不需要必须访问到同一台服务器
- 服务端的集群和状态对客户端透明
- 服务端可以任意的迁移和伸缩(可以方便的进行集群化部署)
- 减小服务端存储压力
流程:
- 首先客户端发送账户名/密码到服务端进行认证
- 认证通过后,服务端将用户信息加密并且编码成一个 token,返回给客户端
- 以后客户端每次发送请求,都需要携带认证的 token
- 服务端对客户端发送来的 token 进行解密,判断是否有效,并且获取用户登录信息
案例可以参考 Spring Security 结合 Jwt 实现无状态登录
交互方式
前后端分离的情况下,交互由传递Jason数据的形式完成
- 登录成功,返回包含成功的信息给前端
- 登录失败,返回包含失败的信息给前端
至于页面的跳转,全部交给前端来完成,与后端无关
登录成功
在上面不分离的情况下,通过successForwardUrl和defaultSuccessUrl来进行跳转,而分离的情况下使用successHandler可以完成两者全部功能
.loginPage("/login.html")//配置登录页和默认的登录接口
.successHandler((req,resp,authentication) ->{
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter respWriter = resp.getWriter();
respWriter.write(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(principal));
respWriter.flush();
respWriter.close();
})
successHandler 方法的参数是一个 AuthenticationSuccessHandler 对象,这个对象中我们要实现的方法是 onAuthenticationSuccess,上面直接lambda表达式写了
onAuthenticationSuccess 方法有三个参数,分别是:
- HttpServletRequest
- HttpServletResponse
- Authentication
前两个参数,利用 HttpServletRequest 我们可以做服务端跳转,利用 HttpServletResponse 我们可以做客户端跳转,当然,也可以返回 JSON 数据。
第三个参数Authentication 则保存了我们刚刚登录成功的用户信息。
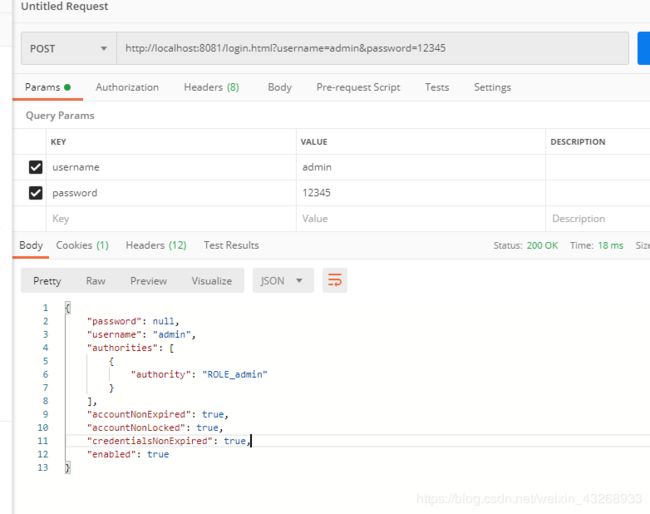
用postman进行测试,获取用户信息,上面的principal可以返回任意自定义的信息
登录失败
登录失败对应的就是failureHandler,代码与上面类似
.failureHandler((req,resp,e)->{
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter respWriter = resp.getWriter();
respWriter.write(e.getMessage());
respWriter.flush();
respWriter.close();
})
例如密码错误的情况下效果
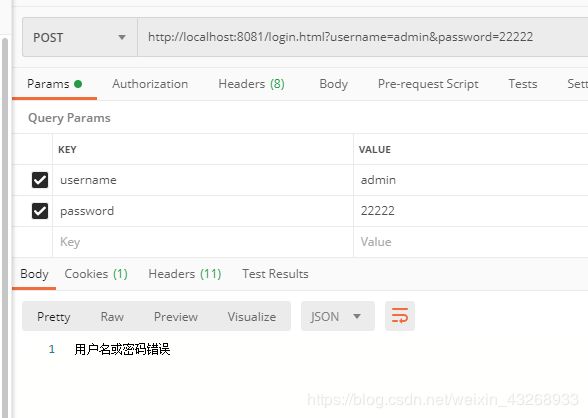
失败的回调也是三个参数,前两个就不用说了,第三个是一个 Exception,对于登录失败,会有不同的原因,Exception 中则保存了登录失败的原因,我们可以将之通过 JSON 返回到前端,我们也可以通过异常的类型来返回不同的信息交给前端处理,例如如下案例写法
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
RespBean respBean = RespBean.error(e.getMessage());
if (e instanceof LockedException) {
respBean.setMsg("账户被锁定,请联系管理员!");
} else if (e instanceof CredentialsExpiredException) {
respBean.setMsg("密码过期,请联系管理员!");
} else if (e instanceof AccountExpiredException) {
respBean.setMsg("账户过期,请联系管理员!");
} else if (e instanceof DisabledException) {
respBean.setMsg("账户被禁用,请联系管理员!");
} else if (e instanceof BadCredentialsException) {
respBean.setMsg("用户名或者密码输入错误,请重新输入!");
}
out.write(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(respBean));
out.flush();
out.close();
未登录的情况
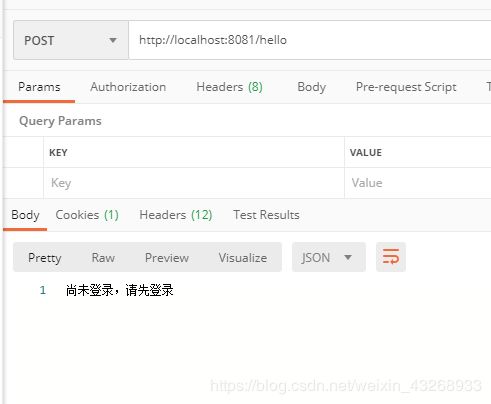
在未登录的情况下,可以给前端返回一个未登录的Jason,再交由前端决定如何跳转
.csrf().disable()
.exceptionHandling()
.authenticationEntryPoint((req, resp, authException) -> {
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
out.write("尚未登录,请先登录");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
);
注销操作
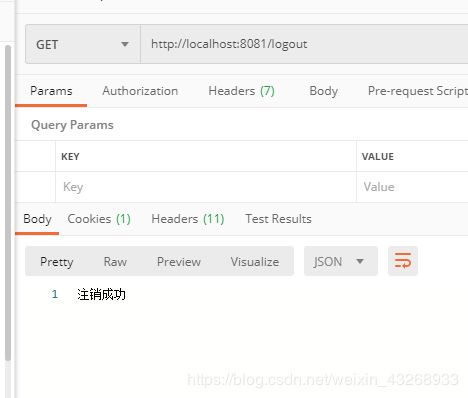
注销操作可以给前端返回一个注销的Jason,再由前端决定如何跳转
.logout()
.logoutUrl("/logout")
.logoutSuccessHandler((req, resp, authentication) -> {
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
out.write("注销成功");
out.flush();
out.close();
})