用C语言解决快速排序问题
快速排序分为三个部分:1,分解即分为三段 2,递归求解:通过递归进行排序 3,合并:将排好序的区间进行合并
递归进行排序
即:void QuickSort(){
if(p int q = Partition(Type ) QuickSort(a , p , q - 1) QuickSort(a , q + 1 , r) //分成了三段 } } Partition是通过基准元素对数组a进行划分的 是排序算法的关键。 算法对a[P:R]进行划分时,通过以元素X=a[ p ]作为划分的基准。 分别从左右两端开始拓展两个区域,再拓展两个区间左边区间的小于基准元素,右边区间的大于基准元素 其中区间大小不断减小,一直循环到左右区间里元素接近 数据结构中源代码如下: #include void quickSort1(int* root, int low, int high) } } int main() 按照算法书上的写法 #include void quickSort1(int* root, int low, int high) } 不需要考虑文件名 我的文件名写错了
{
int pat = root[low];
if (low
int i = low, j = high;
while (i
while (i
j--;
root[i] = root[j];
while (i
root[j] = root[i];
root[i] = pat;
quickSort1(root, low, i - 1);
quickSort1(root, i + 1, high);
}
{
/*int a[8]={4,2,6,7,9,5,1,3}; */
int n;
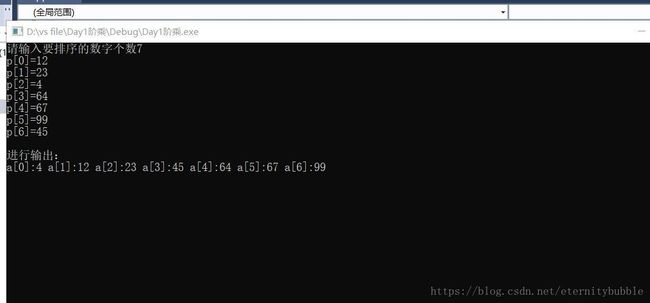
printf("请输入要排序的数字个数");
scanf_s("%d", &n);
int *p = new int[n];
//delete[]p;
for (int i = 0; i
printf("p[%d]=", i);
scanf_s("%d", &*(p + i));
}
printf("\n");
quickSort1(p, 0, n - 1);
//quickSort2(a,0,7);
int i;
printf("进行输出:\n");
for (i = 0; i
printf("a[%d]:%d ", i, p[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
void swap(int &a, int &b)
{
int temp;
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
int Partition(int* a, int low, int high){
int i = low, j = high + 1;
int x = a[low];
while (true){
while (a[++i] < x&&i < high);
while (a[--j]>x);
if (i >= j)break;
swap(a[i], a[j]);
}
a[low] = a[j];
a[j] = x;
return j;
}
{
if (low < high){
int q = Partition(root, low, high);
/*int pat = root[low];
if (low
int i = low, j = high;
while (i
while (i
j--;
root[i] = root[j];
while (i
root[j] = root[i];
root[i] = pat;*/
quickSort1(root, low, q - 1);
quickSort1(root, q + 1, high);
}
}
int main()
{
/*int a[8]={4,2,6,7,9,5,1,3}; */
int n;
printf("请输入要排序的数字个数");
scanf_s("%d", &n);
int *p = new int[n];
//delete[]p;
for (int i = 0; i
printf("p[%d]=", i);
scanf_s("%d", &*(p + i));
}
printf("\n");
quickSort1(p, 0, n - 1);
//quickSort2(a,0,7);
int i;
printf("进行输出:\n");
for (i = 0; i
printf("a[%d]:%d ", i, p[i]);
}
printf("\n");
int k;
scanf_s("%d", &k);
return 0;
}